
Prepositions can be very confusing because they are a few of them and used in many different events. According to research done on 55 students, only 18.18% can be classified as excellent in using prepositions in a sentence.
Prepositions show how and when an event occurred in a sentence. They connect actions, relationships to people, or things that did them.
In this article, you’ll learn about all the types of prepositions and their usage in a sentence using examples. Let’s start!
Related: Types of Adverbs | Types of Diction | Types of Adjectives | Types of Verbs | Types of Pronouns | Types of Conjunctions | Types of Nouns
Types of preposition
Prepositions of Place

Prepositions of place refer to the location of something or someone. In the English language, there are only three prepositions of place. However, they can be of use in a wide range of descriptions.
These prepositions are:
At
This shows a specific/ particular point
In
This shows an enclosed place.
On
It is used to discuss a surface.
Prepositions of place allow you to give a detailed location of something in a narration. Let’s look at how they are used in a sentence:
- I was at the gate when the bell rang.
- The police locked up the thief in a cell.
- I saw the apple on the table.
Prepositions of Time

These prepositions show when something happened (past), is happening (present), or will happen (future). There are several prepositions of time, which include:
At
This preposition is used to show the time.
For example: at 2 am, at noon, etc.
On
It is used to show dates and holidays.
For example: on 12 January, on Christmas day, etc.
In
This preposition of time is used to show more prolonged periods.
For example: in the morning, in summer, etc.
During
When you add a noun, the preposition shows when something happened.
For example: during the break, during the game, etc.
For
This preposition shows the duration of time when combined with a noun.
For example: for years, for months, etc.
Since
We combine since and a noun to show a specific time when something began.
For example: since 1945, since January, etc.
Until
It is used to show the duration for which something has happened or has been happening.
For example: until the sun goes down; until I convince him.
From and to
It shows the start to the end.
For example: from January to March, from 1940 to 2020.
Example in a sentence;
- Obama served as president for four years.
- United Nations organization has been in existence since 1946
Preposition of direction
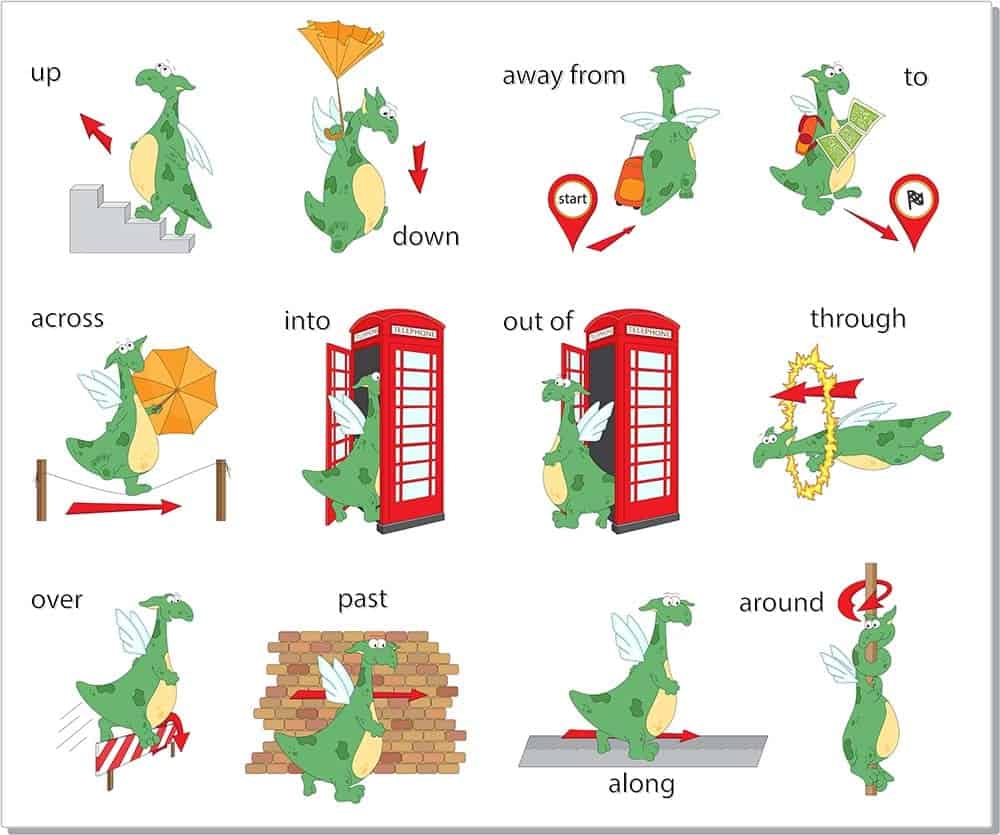
These prepositions indicate the motion of something or someone. There are several prepositions of direction, but we will only cover the most common ones. Preposition of direction includes: above, across along, among, around, at, behind, below, beside, close, through, toward, up, down, between, by, inside, near, next, to, onto, off, past, and under. Get a diagrammatic explanation here and learn how to use prepositions from Grammarly here.
To
It’s the most common directional preposition and does not show any specific direction.
Into
This preposition that shows movement that gets inside or looks inside.
Across
Shows movement from one side to the other.
Through
The preposition shows movement from outside to inside or inside to outside.
Examples in a sentence;
- I went to the market and bought some vegetables.
- He poured the water into the glass.
- I run across the road the road
- The bullet went through the wall to the child.
Preposition of manner
Preposition of manner shows how something happened or is done in a sentence. These prepositions include: by, in, like, with, and on. However, the most common prepositions of manner are: by and with.
The preposition “by” shows how or in what way something happened. On the other hand, the preposition “with” is interpreted to mean “in the company of someone.”
Here are several example sentences using prepositions of manner;
- We went to school by bus
- We reacted with anger to his abuse.
- The president arrived on the island on a ferry.
Preposition of measure
These prepositions indicate the relationship between the quantity of something and someone or something else. They are used in measurements or when comparing sizes. Prepositions of manner include: by, at, and of.
By
Shows standard measurements or value and sometimes in comparing sizes.
At
Used with exact measurements.
Of
Shows an abstract measurement that cannot be in numbers.
Here are some examples in a sentence;
- That bank charges interest rates at 12%.
- She is taller than me by 12 inches.
- His inheritance was a piece of land.
Preposition of source
Prepositions of source indicate the origin of something or someone when used in a sentence. These prepositions include from and by.
Example in a sentence;
- The kidnappers emerged from the bush.
- His car was bought by my wife.

Preposition of possession
These prepositions explain that something belongs to someone or something else. They show ownership. They include: of, to, and with. In some cases, we use them alongside the word “belong.”
Here some examples in a sentence;
- I saw the boy with a radio.
- That is the car of my dreams
- He is the boy with the piercing on his nose
- That house belongs to his boss
Preposition of agent of instrument
Prepositions of agents of instrument show us who or what did a particular action. They help you associate a specific activity with someone or something; they connect the doer and the action. They include;
By
Shows action done by a person in a sentence
With
They relate an action with a thing.
Examples in a sentence:
- Rich Dad Poor Dad was written by Robert Kiyosaki
- The bull injured him with its horns
To summarize, prepositions can be very confusing and embarrassing, especially when you’re communicating. On the other hand, proper usage of preposition shows great prowess and mastery of the language. The eight prepositions will help you learn the art of using them properly and boost your writing and communicating confidence.
FAQs
Do you say “I’m on a plane” or “I’m in a plane.”
“I’m on a plane” is the correct way to say it. “On” is one of the trickiest prepositions. It’s funny because the wings too are on the plane, and the logo is also on the plane.
Is ending a sentence with a preposition a grammatical error?
No. However, ending a sentence with a preposition sounds informal. You can end with a preposition in texts, emails, and friendly notes but probably not in your research paper. You can get more information here.
Should prepositions be capitalized in titles?
No. Prepositions and conjunctions should not be capitalized in titles. However, there are some exceptions.
- They should not be capitalized unless they end or start in a sentence.
- A preposition should be capitalized if it has six letters or more.
You can have more insights here.

Jon Dykstra is a six figure niche site creator with 10+ years of experience. His willingness to openly share his wins and losses in the email newsletter he publishes has made him a go-to source of guidance and motivation for many. His popular “Niche site profits” course has helped thousands follow his footsteps in creating simple niche sites that earn big.





